Table of Contents
Additive manufacturing and rapid prototyping are two terms that are often used interchangeably, but they are not the same thing. While both processes involve creating three-dimensional objects from digital designs, there are some significant differences that set them apart.
Additive manufacturing is a process of building objects layer by layer through the use of a variety of materials, including plastics, metals, and even living cells. Rapid prototyping, on the other hand, is a subset of additive manufacturing that is focused on quickly creating prototypes or models of products. In this article, we will explore the differences between these two processes and how they are being used in industries ranging from aerospace to healthcare.
Additive manufacturing and rapid prototyping are often used interchangeably, but they are not the same. Rapid prototyping is a subset of additive manufacturing, where a physical model is quickly created to test a design. On the other hand, additive manufacturing is a broader term that refers to the process of creating a three-dimensional object by adding layers of material. Additive manufacturing can be used for production purposes, whereas rapid prototyping is primarily used for testing and design validation.
How Does Additive Manufacturing Differ From Rapid Prototyping?
Additive manufacturing and rapid prototyping are two terms that are often used interchangeably. However, these two processes are not the same. While they have some similarities, there are some key differences between them. In this article, we will explore how additive manufacturing differs from rapid prototyping.
What is Additive Manufacturing?
Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, is the process of creating a three-dimensional object by adding material layer by layer. The process starts with a digital 3D model of the object that is created using computer-aided design (CAD) software. This digital model is then sliced into layers, and the 3D printer creates the object by adding material layer by layer until the final object is complete.
There are several different types of additive manufacturing technologies, including fused deposition modeling (FDM), stereolithography (SLA), and selective laser sintering (SLS). Each of these technologies uses different materials and methods to create objects.
Benefits of Additive Manufacturing
– Additive manufacturing allows for the creation of complex geometries that would be difficult or impossible to produce using traditional manufacturing methods.
– It can create objects with a high degree of accuracy and precision.
– It is a cost-effective way to produce small batches of custom parts.
– Additive manufacturing is a flexible process that can be used to create a wide range of objects, from small toys to large aerospace components.
What is Rapid Prototyping?
Rapid prototyping is a process that is used to quickly create a physical prototype or model of a product. The process starts with a 3D CAD model of the object, which is then used to create a physical model using a rapid prototyping machine. The machine creates the model by adding material layer by layer, similar to the additive manufacturing process.
Rapid prototyping is often used in product development to create prototypes for testing and evaluation. It allows designers to quickly iterate on designs and make changes without the need for expensive tooling.
Benefits of Rapid Prototyping
– Rapid prototyping allows for quick iterations and design changes, which can save time and money in the product development process.
– It can help identify design flaws and potential manufacturing issues early in the development process.
– It allows for physical testing and evaluation of the product before investing in expensive tooling and manufacturing.
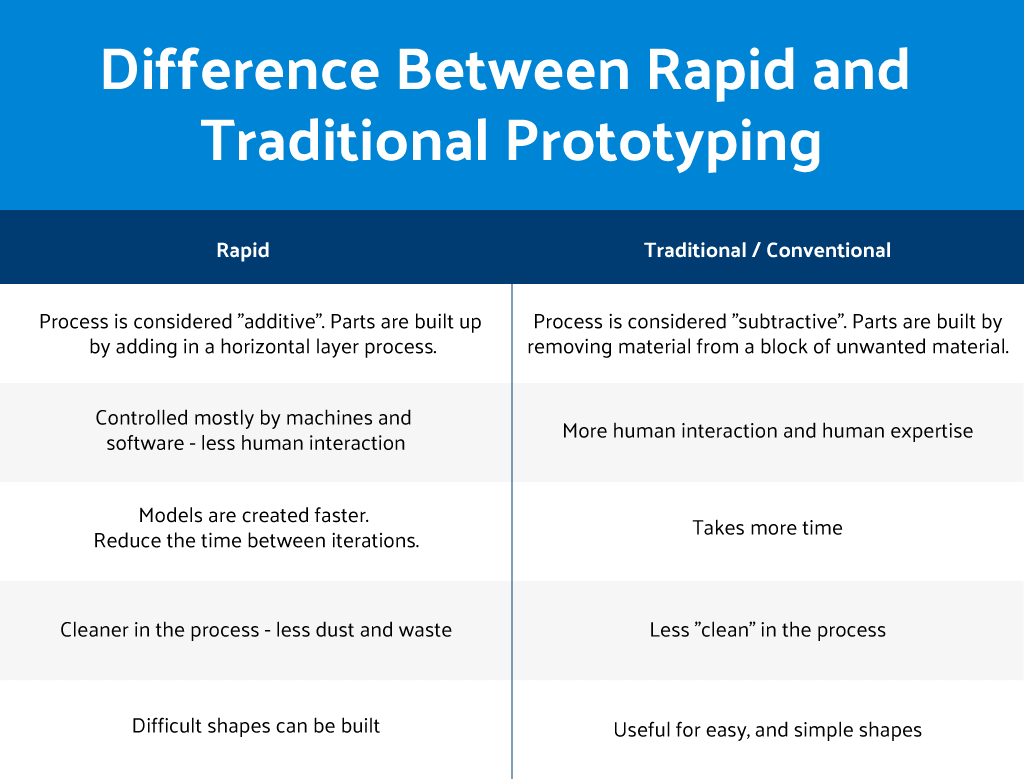
The Differences Between Additive Manufacturing and Rapid Prototyping
While additive manufacturing and rapid prototyping share some similarities, there are some key differences between them.
Additive Manufacturing vs. Rapid Prototyping
| Additive Manufacturing | Rapid Prototyping |
|---|---|
| Used to create finished products | Used to create prototypes |
| Can be used to create complex geometries | Can be used to create simple geometries |
| Requires more time and resources | Requires less time and resources |
| Allows for customization and personalization | Used for testing and evaluation |
Conclusion
In conclusion, additive manufacturing and rapid prototyping are two distinct processes that serve different purposes. Additive manufacturing is used to create finished products, while rapid prototyping is used to create prototypes for testing and evaluation. While they share some similarities, the differences between the two processes are significant. By understanding these differences, designers and manufacturers can choose the right process for their specific needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
In the world of manufacturing, there are many different techniques and technologies that are used to create products. Two of the most popular are additive manufacturing and rapid prototyping. While they are similar in many ways, there are also some key differences between the two. In this article, we will explore some of the most frequently asked questions about how additive manufacturing differs from rapid prototyping.
What is Additive Manufacturing?
Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, is a process of creating objects by adding layers of material on top of each other. This is done using a computer-aided design (CAD) model, which is broken down into individual layers. The printer then creates each layer one at a time, building up the object until it is complete.
One of the key benefits of additive manufacturing is that it allows for a high degree of customization. Because the object is built layer by layer, it is possible to create complex shapes and designs that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional manufacturing techniques. Additive manufacturing is also faster and more cost-effective than many other methods, making it a popular choice for producing prototypes and small batches of products.
What is Rapid Prototyping?
Rapid prototyping is a process of creating physical prototypes of a product using a variety of techniques. These techniques can include 3D printing, CNC machining, and other methods. The goal of rapid prototyping is to quickly create a physical model of a product so that it can be tested and evaluated before moving on to mass production.
One of the key benefits of rapid prototyping is that it allows for rapid iteration and testing. Because prototypes can be created quickly and inexpensively, it is possible to make changes and improvements to a product design without significant cost or time delays. Rapid prototyping is also useful for creating custom parts or products that require a high degree of precision or complexity.
How Does Additive Manufacturing Differ From Rapid Prototyping?
Additive manufacturing is a type of rapid prototyping, but not all rapid prototyping uses additive manufacturing. While both processes are used to create physical models of products, additive manufacturing specifically refers to the use of 3D printing to build up an object layer by layer. Rapid prototyping can include a variety of techniques, including 3D printing, CNC machining, and other methods.
Another key difference between additive manufacturing and rapid prototyping is that additive manufacturing is typically faster and more cost-effective than other rapid prototyping techniques. This is because 3D printing can create complex shapes and designs with minimal setup time or tooling costs. Rapid prototyping using other methods, such as CNC machining, may require more time and resources to set up and produce a prototype.
What Are the Benefits of Additive Manufacturing?
Additive manufacturing offers several benefits over traditional manufacturing techniques. One of the biggest benefits is that it allows for a high degree of customization and complexity. Because objects can be built layer by layer, it is possible to create intricate designs and shapes that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with other methods.
Additive manufacturing is also faster and more cost-effective than many other methods, especially for small batches or custom parts. Because there is minimal setup time or tooling required, it is possible to produce a prototype or small batch of parts quickly and inexpensively. This makes additive manufacturing a popular choice for prototyping and low-volume production runs.
What Are the Benefits of Rapid Prototyping?
Rapid prototyping offers several benefits over traditional product development methods. One of the biggest benefits is that it allows for rapid iteration and testing. Because prototypes can be created quickly and inexpensively, it is possible to make changes and improvements to a product design without significant cost or time delays.
Rapid prototyping is also useful for creating custom parts or products that require a high degree of precision or complexity. By using advanced manufacturing techniques such as 3D printing or CNC machining, it is possible to create parts with a high degree of accuracy and consistency. This makes rapid prototyping a popular choice for industries such as aerospace, medical devices, and automotive manufacturing.
In conclusion, additive manufacturing and rapid prototyping are two processes that have revolutionized the manufacturing industry. While they share some similarities, they differ in key ways.
Additive manufacturing is the process of creating a three-dimensional object by adding layers of material. It is a more advanced and sophisticated process that allows for the creation of complex and intricate designs. Rapid prototyping, on the other hand, is a simpler process that involves creating a physical model of a design using a 3D printer.
One of the main advantages of additive manufacturing is the ability to produce high-quality, functional parts with minimal waste. This is in contrast to rapid prototyping, which is more suited for creating prototypes and models for testing and evaluation purposes. Therefore, the choice between the two processes depends on the specific needs of the manufacturer.
Overall, additive manufacturing offers a range of benefits that make it an attractive option for manufacturers looking to produce complex, high-quality parts. While rapid prototyping still has its place in the industry, additive manufacturing is quickly becoming the go-to method for creating functional parts and products.
Request a quote today!
[contact-form-7 id="1578" title="Contact form"]
Please compress the file into a ZIP or RAR file before uploading. Alternatively, send through your RFQ by email.
enquires@unitymanufacture.com