Table of Contents
Extruded aluminum is a versatile material that offers a range of benefits, including excellent strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and easy machinability. However, when it comes to thin profiles, many wonder just how thin extruded aluminum can be.
The answer, it turns out, depends on a variety of factors, including the alloy used, the shape of the profile, and the extrusion process itself. In this article, we’ll explore the world of thin extruded aluminum profiles, from the thinnest possible profiles to the practical limits of extrusion technology.
How Thin Can Extruded Aluminum Be?
Extruded aluminum is a versatile and widely used material in various industries. It is known for its strength, durability, and lightweight properties. One of the most common questions asked about extruded aluminum is how thin it can be made. In this article, we will explore the answer to this question and the factors that affect the thickness of extruded aluminum.
The Basics of Extruded Aluminum
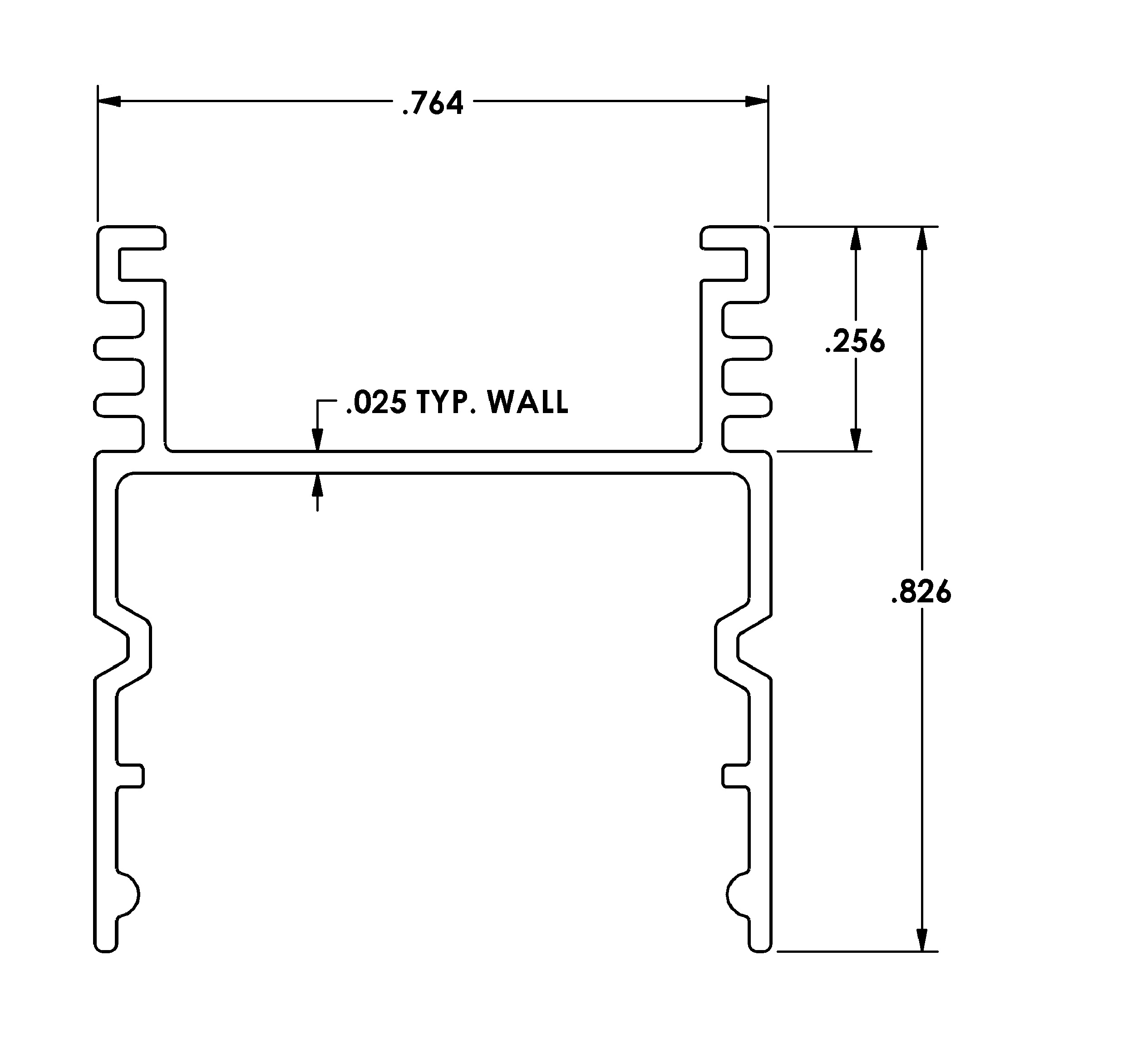
Extruded aluminum is created by forcing a heated aluminum billet through a die to form a specific shape or profile. The process of extrusion involves applying high pressure to the billet and pushing it through the die until it takes on the desired shape. Extruded aluminum can be made into a wide range of shapes, from simple tubes and rods to complex profiles with intricate designs. The thickness of the extruded aluminum depends on the size and complexity of the shape being produced.
There are several factors that affect the thickness of extruded aluminum. These include the type of alloy used, the shape and design of the die, the temperature of the billet, and the speed of the extrusion process. Let’s dive deeper into these factors to understand how they impact the thickness of extruded aluminum.
The Type of Alloy Used
The type of alloy used in the extrusion process can affect the thickness of the final product. Different alloys have different properties that can impact how easily they can be extruded and at what thicknesses. For example, some alloys have a higher melting point, which can make them more difficult to extrude at thinner thicknesses. Other alloys have a higher ductility, which can allow them to be extruded at thinner thicknesses without cracking or breaking.
Alloys that are commonly used in extruded aluminum include 6061, 6063, and 7075. These alloys have different properties and are used for different applications. 6061 and 6063 are commonly used for architectural and structural applications, whereas 7075 is used for high-stress applications such as aerospace and defense.
The Shape and Design of the Die
The shape and design of the die used in the extrusion process can also impact the thickness of the final product. Dies can be made in various shapes and designs to accommodate different shapes and thicknesses of extruded aluminum. The size and complexity of the shape being produced can also affect the thickness of the final product. For example, simple shapes like tubes and rods can be extruded at thinner thicknesses than complex profiles with intricate designs.
It’s important to note that the design of the die can also impact the quality of the final product. Poor die design can result in defects such as surface imperfections, uneven thicknesses, and warping. This can impact the performance and durability of the extruded aluminum.
The Temperature of the Billet
The temperature of the billet used in the extrusion process can also impact the thickness of the final product. The billet needs to be heated to a specific temperature to make it malleable enough to be extruded. If the billet is not heated to the correct temperature, it may not extrude evenly or at the desired thickness. Temperature also plays a role in the speed of the extrusion process. If the billet is too hot, it may extrude too quickly and result in thinner walls than intended. If the billet is too cold, it may not extrude at all.
The optimal temperature for extruding aluminum depends on the specific alloy being used and the shape being produced. The temperature is often monitored closely during the extrusion process to ensure that the billet is heated to the correct temperature and that the extrusion process is proceeding as intended.
The Speed of the Extrusion Process
The speed of the extrusion process can also impact the thickness of the final product. If the extrusion process is too slow, the walls of the extruded aluminum may become thicker than intended. If the extrusion process is too fast, the walls may become thinner than intended. The speed of the extrusion process needs to be carefully controlled to ensure that the extruded aluminum is produced at the desired thickness.
The speed of the extrusion process can be impacted by several factors, including the temperature of the billet, the shape and design of the die, and the type of alloy being used. It’s important to monitor the speed of the extrusion process closely to ensure that the final product is produced at the desired thickness.
Benefits of Thin Extruded Aluminum
Thin extruded aluminum can offer several benefits in various applications. For example, thin-walled aluminum tubing is commonly used in the automotive industry to reduce weight and improve fuel efficiency. Thin extruded aluminum profiles can also be used to create complex shapes and designs that would be difficult to achieve with other materials.
Thin extruded aluminum can also be cost-effective, as it requires less material and energy to produce than thicker profiles. This can be particularly advantageous in high-volume applications where cost savings are important.
Extruded Aluminum vs. Other Materials
Extruded aluminum offers several advantages over other materials such as steel and plastic. Aluminum is lighter and more durable than steel, making it ideal for applications where weight is a concern. Extruded aluminum is also more environmentally friendly than plastic, as it is recyclable and can be reused in other applications. Aluminum also has a higher strength-to-weight ratio than plastic, making it a better choice for applications where strength is important.
Overall, the ability to make extruded aluminum as thin as possible depends on several factors, including the type of alloy used, the shape and design of the die, the temperature of the billet, and the speed of the extrusion process. Thin extruded aluminum can offer several benefits in various applications, including reduced weight, improved fuel efficiency, and cost savings. Extruded aluminum also offers several advantages over other materials such as steel and plastic, making it a popular choice in various industries.
Frequently Asked Questions
Aluminum extrusions have become an essential part of many industrial applications. One of the most common questions about aluminum extrusions is how thin they can be. Below are five questions and answers about this topic.
What is the thinnest aluminum extrusion possible?
The thinnest aluminum extrusion possible mainly depends on the extrusion process and the type of aluminum alloy used. Generally, the thinnest aluminum extrusion possible is about 0.03 inches. However, it is essential to note that thinner extrusions are more challenging to manufacture due to the risk of deformation or breakage during the manufacturing process.
Additionally, the thinner the aluminum extrusion, the less strength it has. Therefore, it is essential to consider the intended use of the extrusion when determining the appropriate thickness.
What factors determine the thickness of an aluminum extrusion?
Several factors determine the thickness of an aluminum extrusion. These factors include the die design, the extrusion process, and the type of aluminum alloy. The die design plays a crucial role in determining the minimum wall thickness of the extrusion. A well-designed die will produce extrusions with uniform wall thickness and minimize the risk of deformation or breakage.
The extrusion process also plays a role in determining the thickness of an aluminum extrusion. Extrusions that undergo a more extensive manufacturing process, such as those that go through multiple passes, are generally thinner. The type of aluminum alloy used can also affect the minimum thickness of an extrusion, with some alloys being more suitable for thin extrusions than others.
What are the benefits of using thin aluminum extrusions?
Thin aluminum extrusions have several benefits, including reduced weight, improved flexibility, and increased cost-effectiveness. Their reduced weight makes them ideal for applications where weight is a critical factor, such as in the aerospace industry. Additionally, their improved flexibility makes them easier to shape into complex designs, making them ideal for applications where aesthetics are essential.
Their increased cost-effectiveness is another benefit of using thin aluminum extrusions. Thin extrusions require less material, energy, and labor to manufacture, making them more cost-effective than thicker extrusions.
What are the challenges of manufacturing thin aluminum extrusions?
Manufacturing thin aluminum extrusions can be challenging due to the risk of deformation or breakage during the manufacturing process. The thinner the extrusion, the more susceptible it is to these risks. Therefore, manufacturers must use appropriate die designs and extrusion processes to minimize these risks.
Additionally, thin extrusions are less robust than thicker extrusions, making them less suitable for applications where strength is critical. Therefore, it is essential to consider the intended use of the extrusion when determining the appropriate thickness.
What industries commonly use thin aluminum extrusions?
Thin aluminum extrusions are commonly used in industries where weight, flexibility, and aesthetics are essential factors. For example, the aerospace industry commonly uses thin aluminum extrusions in aircraft structures to reduce weight while maintaining strength. The automotive industry commonly uses thin extrusions in vehicle frames and body panels to improve fuel efficiency and reduce weight.
The construction industry also commonly uses thin aluminum extrusions in building facades and window frames to improve aesthetics and reduce weight. The electronics industry commonly uses thin extrusions in electronic enclosures to improve heat dissipation and reduce weight.
In conclusion, the answer to the question of how thin extruded aluminum can be depends on a few factors. The extrusion process itself allows for very thin profiles, with some manufacturers able to produce profiles as thin as 0.010 inches. However, the thickness of the final product is also influenced by the alloy used and the application for which it will be used.
Despite these limitations, extruded aluminum is a versatile and durable material that can be used in a wide range of applications, from building facades to automotive components. Its ability to be formed into complex shapes and its high strength-to-weight ratio make it an attractive choice for designers and engineers.
In the end, the question of how thin extruded aluminum can be is less important than understanding the unique properties and capabilities of this material. With the right design and engineering expertise, extruded aluminum can be used to create innovative and efficient solutions for a variety of industries and applications.
Request a quote today!
[contact-form-7 id="1578" title="Contact form"]
Please compress the file into a ZIP or RAR file before uploading. Alternatively, send through your RFQ by email.
enquires@unitymanufacture.com