Table of Contents
- Frequently Asked Questions
- What is Autodesk and how does it relate to CNC machining?
- How do I import a CAD file into Autodesk for CNC machining?
- What are some best practices for using Autodesk for CNC machining?
- Can Autodesk’s CAM software be used with any type of CNC machine?
- What are some resources for learning more about using Autodesk for CNC machining?
Are you trying to master CNC machining with Autodesk? Look no further! With the right tools and techniques, you can streamline your workflow and create precise, high-quality designs in no time. In this guide, we’ll explore the ins and outs of using Autodesk for CNC machining, from setting up your workspace to optimizing your toolpaths for maximum efficiency. Whether you’re a seasoned pro or just starting out, this comprehensive guide has everything you need to take your CNC machining skills to the next level. So, let’s dive in and get started!
How to Use Autodesk for CNC Machining?
To use Autodesk for CNC machining, follow these steps:
- Open Autodesk and create a new project.
- Import your design file into the project.
- Use Autodesk’s CAM tools to generate toolpaths for your CNC machine.
- Simulate the toolpaths to ensure they produce the desired result.
- Export the toolpaths to a format compatible with your CNC machine.
- Load the toolpaths onto your CNC machine and start machining.
How to Use Autodesk for CNC Machining?
Autodesk is a popular software used for Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining. It allows users to create 3D models of their designs and produce them through CNC machines. However, learning how to use Autodesk for CNC machining can be intimidating for beginners. In this article, we will guide you through the process of using Autodesk for CNC machining.
1. Understanding the Interface
The first step in using Autodesk for CNC machining is to understand the interface. The interface consists of several components such as the toolbar, ribbon, and command line. The toolbar contains common tools such as the line, circle, and rectangle tools. The ribbon contains tabs that organize the tools according to their functions. The command line allows users to enter commands directly.
To make the interface more user-friendly, users can customize the workspace by adding or removing tools and changing their location. By understanding how the interface works, users can navigate through the software with ease.
2. Creating a 3D Model
The next step in using Autodesk for CNC machining is to create a 3D model. Users can create a 3D model by using the various tools available in the software. They can create shapes such as rectangles, circles, and polygons, and then extrude or revolve them to form 3D objects.
Users can also import 3D models from other software such as SolidWorks or AutoCAD. Once they have created or imported a 3D model, they can modify it using tools such as fillet, chamfer, and shell.
3. Setting up the CNC Machine
Before producing the 3D model, users need to set up the CNC machine. This involves creating a toolpath that the machine will follow. The toolpath determines the cutting tool’s movement and the material’s removal.
Users can create a toolpath by using the CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) feature in Autodesk. The CAM feature allows users to generate toolpaths based on the 3D model’s geometry, material, and cutting tool. They can adjust the toolpath’s parameters such as the feed rate, cutting depth, and spindle speed.
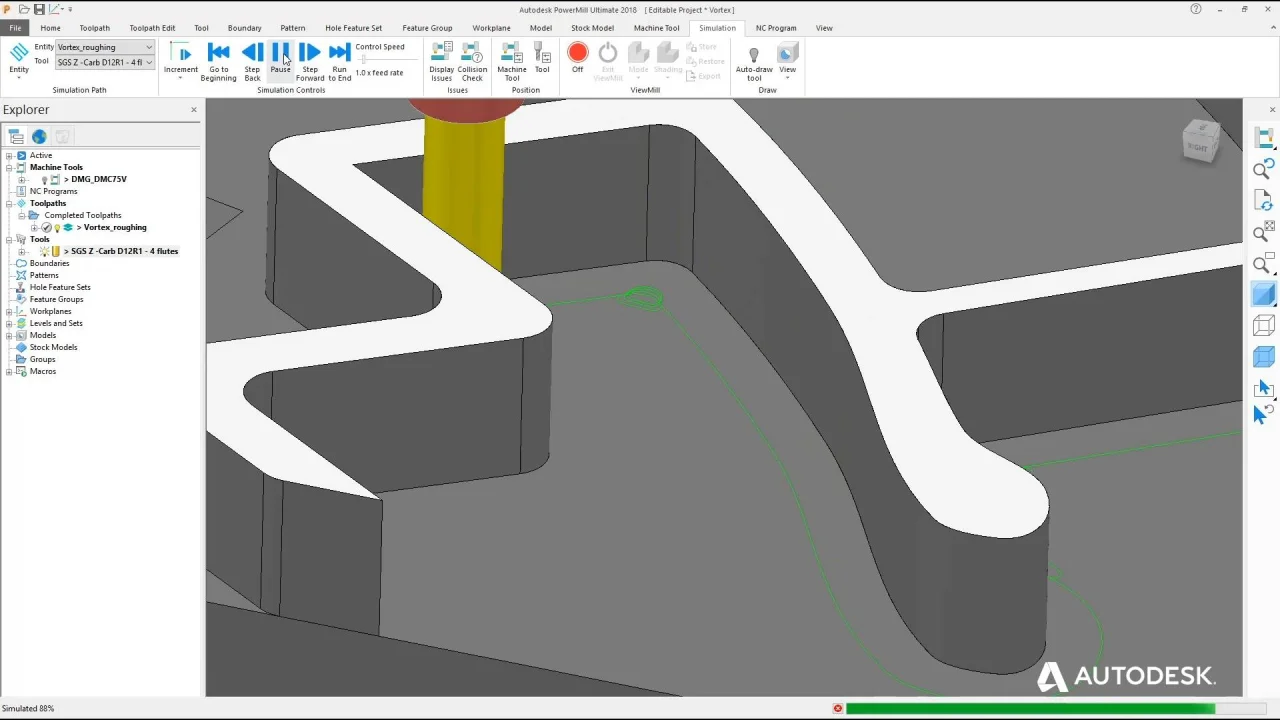
4. Simulating the Toolpath
After creating the toolpath, users need to simulate it to ensure that it is correct. The simulation allows users to visualize the tool’s movement and the material’s removal. They can detect any potential problems such as tool collisions or excessive material removal.
Users can simulate the toolpath by using the CAM feature in Autodesk. The CAM feature allows users to preview the tool’s movement in a 3D environment. They can adjust the simulation’s parameters such as the speed, tool diameter, and material’s color.
5. Generating the G-code
Once the simulation is complete, users can generate the G-code. The G-code is a language that the CNC machine understands. It contains the toolpath’s information such as the movement, speed, and cutting depth.
Users can generate the G-code by using the Post Processor feature in Autodesk. The Post Processor feature allows users to convert the toolpath into a G-code file. They can select the appropriate file format that the CNC machine uses.
6. Transferring the G-code to the CNC Machine
After generating the G-code, users need to transfer it to the CNC machine. This involves connecting the computer to the CNC machine and uploading the G-code file.
Users can transfer the G-code by using a USB cable, Ethernet cable, or Wi-Fi. They can select the appropriate transfer method based on the CNC machine’s specifications.
7. Starting the CNC Machine
Once the G-code is uploaded, users can start the CNC machine. They need to ensure that the machine is properly calibrated and the cutting tool is securely attached.
Users can start the CNC machine by using the control panel. They can select the appropriate program and press the start button. They need to monitor the machine’s operation and make any necessary adjustments.
8. Benefits of Using Autodesk for CNC Machining
Using Autodesk for CNC machining has several benefits. Firstly, it allows users to create complex 3D models with ease. Secondly, it provides a user-friendly interface that makes the software easy to use. Thirdly, it allows users to simulate the toolpath and detect any potential problems. Fourthly, it generates accurate G-code that ensures the CNC machine produces the correct part. Lastly, it provides a seamless workflow from design to production.
9. Autodesk for CNC Machining Vs. Other Software
Compared to other software, Autodesk for CNC machining has several advantages. Firstly, it provides a complete solution that includes 3D modeling, simulation, and CAM. Secondly, it has a user-friendly interface that makes the software easy to use. Thirdly, it provides accurate G-code that ensures the CNC machine produces the correct part. Lastly, it provides a seamless workflow from design to production.
10. Conclusion
In conclusion, using Autodesk for CNC machining is an excellent choice for beginners and professionals alike. By understanding the interface, creating a 3D model, setting up the CNC machine, simulating the toolpath, generating the G-code, transferring the G-code to the CNC machine, and starting the CNC machine, users can produce high-quality parts with ease. The benefits of using Autodesk for CNC machining and its advantages over other software make it a top choice for CNC machining.
Frequently Asked Questions
In this section, we will answer the most common questions related to using Autodesk for CNC machining.
What is Autodesk and how does it relate to CNC machining?
Autodesk is a software company that produces various software products, including software for computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM). Autodesk’s software products can be used in various industries, including CNC machining.
Autodesk’s CAM software, such as Fusion 360 and PowerMill, can be used to generate toolpaths for CNC machines. These toolpaths are used by the CNC machine to carve out the desired shape from the raw material.
How do I import a CAD file into Autodesk for CNC machining?
To import a CAD file into Autodesk for CNC machining, you first need to ensure that the file is in a format that is compatible with Autodesk’s software. Common file formats that Autodesk’s software can import include .STL, .STEP, and .IGES.
Once you have a compatible CAD file, you can import it into Autodesk’s software using the “Import” function. From there, you can use the software’s CAM tools to generate toolpaths for the CNC machine.
What are some best practices for using Autodesk for CNC machining?
Some best practices for using Autodesk for CNC machining include: becoming familiar with the software’s interface and capabilities, properly setting up your machine and tooling parameters, and testing your toolpaths before running them on the actual machine.
Additionally, it is important to keep your software up-to-date and to stay current with industry trends and advancements in CNC machining technology.
Can Autodesk’s CAM software be used with any type of CNC machine?
Autodesk’s CAM software can be used with a wide range of CNC machines, including mills, lathes, routers, and plasma cutters. However, it is important to ensure that your specific CNC machine is compatible with Autodesk’s software before purchasing or using it.
Additionally, it may be necessary to customize the software’s settings and parameters to match the specific capabilities and limitations of your CNC machine.
What are some resources for learning more about using Autodesk for CNC machining?
There are many resources available for learning more about using Autodesk for CNC machining, including online tutorials, forums, and user groups. Autodesk’s website also provides a wealth of information and resources, including documentation, webinars, and training courses.
Additionally, it may be helpful to seek out mentorship or guidance from experienced professionals in the field of CNC machining.
In conclusion, Autodesk is a powerful tool for CNC machining that can greatly enhance your productivity and efficiency. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can start using Autodesk to create precise and accurate designs for your CNC machines. With Autodesk’s advanced features and easy-to-use interface, you can take your machining projects to the next level and create high-quality parts with ease.
As you become more familiar with Autodesk, you will begin to discover even more ways to streamline your workflow and optimize your designs. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced machinist, Autodesk has everything you need to succeed in the world of CNC machining. So why wait? Start exploring Autodesk today and see what it can do for you!
In the end, mastering Autodesk for CNC machining is a valuable skill that can help you advance your career and achieve your goals. With its powerful tools and intuitive interface, Autodesk is the ideal software for anyone looking to take their machining projects to the next level. So don’t hesitate – start using Autodesk today and see for yourself why it’s the go-to choice for machinists around the world!
Request a quote today!
[contact-form-7 id="1578" title="Contact form"]
Please compress the file into a ZIP or RAR file before uploading. Alternatively, send through your RFQ by email.
enquires@unitymanufacture.com