Table of Contents
Die casting is a manufacturing process that involves pouring molten metal into a mold cavity under high pressure. The metal solidifies quickly, taking the shape of the mold and creating a finished product with a high level of accuracy and detail.
This technique has been used for centuries to produce a wide range of metal products, from small components to large industrial parts. Today, die casting is widely used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics, and is known for its efficiency, precision, and durability.
H2: What is Die Casting?
Die casting is a manufacturing process that involves the production of metal parts by forcing molten metal under high pressure into molds, also known as dies. This process is widely used in the production of a range of products, including automobiles, toys, and household appliances. With die casting, manufacturers can create complex shapes and designs with high precision and accuracy.
H3: How Does Die Casting Work?
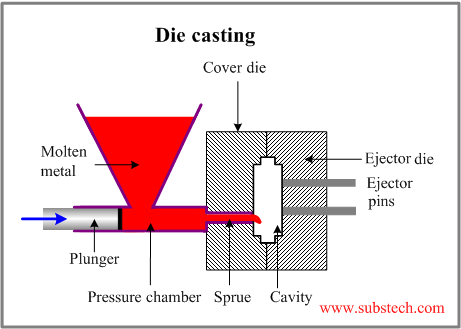
Die casting involves several stages, including mold preparation, melting of the metal, injection, solidification, and ejection. The process starts with the creation of the mold, which is made of two parts that fit together to create a cavity in the desired shape. The mold is then coated with a lubricant to prevent the metal from sticking to its surface.
Next, the metal is melted in a furnace and then injected into the mold using high pressure. The metal fills the cavity and takes the shape of the mold. As the metal cools and solidifies, it contracts and pulls away from the walls of the mold, creating the desired shape. Once the metal has cooled sufficiently, the mold is opened, and the part is ejected.
H3: Types of Die Casting
There are two main types of die casting: hot chamber and cold chamber. Hot chamber die casting is used for metals with low melting points, such as zinc, while cold chamber die casting is used for metals with high melting points, such as aluminum and copper.
Hot chamber die casting involves the use of a furnace that is attached to the die casting machine. The metal is melted in the furnace, and then a piston injects it into the mold. Cold chamber die casting, on the other hand, involves the use of a separate furnace to melt the metal, which is then manually transferred to the injection chamber.
H3: Benefits of Die Casting
Die casting offers several benefits over other manufacturing processes. For one, it allows for the production of complex shapes and designs with high precision and accuracy. It also offers a high production rate, making it an efficient and cost-effective process for mass production.
Die casting also offers excellent dimensional accuracy and repeatability, which is essential for ensuring consistency in the quality of the parts produced. Additionally, it results in parts with excellent surface finishes, which can reduce the need for additional finishing processes.
H3: Die Casting vs. Other Manufacturing Processes
Die casting offers several advantages over other manufacturing processes. For example, it is faster and more efficient than sand casting, which involves the use of a mold made of sand. It also offers better dimensional accuracy and surface finishes than investment casting, which uses a wax model to create the mold.
Injection molding is another manufacturing process that is often compared to die casting. While both processes involve the injection of molten material into a mold, injection molding is typically used for the production of plastics, while die casting is used for metals. Die casting also offers better surface finishes and dimensional accuracy than injection molding.
H3: Applications of Die Casting
Die casting is used in the production of a wide range of products, including automotive parts, toys, household appliances, and electronics. In the automotive industry, die casting is used to produce engine blocks, transmission cases, and other components. In the electronics industry, it is used to produce computer parts, cell phone housings, and other components.
Die casting is also used in the production of household appliances, such as refrigerators, washing machines, and air conditioners. It is an efficient and cost-effective process for producing large quantities of high-quality parts.
H3: Advancements in Die Casting Technology
Over the years, there have been several advancements in die casting technology that have improved the process and made it more efficient. For example, the use of computer-aided design (CAD) software has made it easier to design and create molds with complex shapes and designs.
The use of robotics has also improved the efficiency of the process by automating many of the tasks involved in die casting. Additionally, the use of high-pressure die casting has made it possible to produce parts with thinner walls and more complex geometries.
H3: Conclusion
Die casting is a versatile and efficient manufacturing process that has revolutionized the production of metal parts. With its ability to produce complex shapes and designs with high precision and accuracy, die casting has become a popular choice for a wide range of industries. Advancements in die casting technology continue to improve the process, making it faster, more efficient, and more cost-effective than ever before.
Freequently Asked Questions
Die casting is a manufacturing process in which a molten metal is injected into a mold cavity under high pressure. The metal then solidifies and takes the shape of the mold, creating a final product.
What materials are commonly used in die casting?
The most commonly used materials in die casting are zinc, aluminum, and magnesium. These materials have a low melting point, making them easy to cast, and they can also be easily formed into complex shapes. Other materials, such as copper and brass, can also be used in die casting, but they are less common.
When selecting a material for die casting, it is important to consider factors such as strength, durability, and cost. Zinc is often used for small parts, while aluminum is a popular choice for larger parts due to its lightweight and high strength-to-weight ratio. Magnesium is also a lightweight material that is often used in automotive and aerospace applications.
What are the advantages of die casting?
There are several advantages to using die casting as a manufacturing process. First, it allows for the creation of complex shapes with a high degree of accuracy and consistency. Die casting also produces parts with a smooth surface finish, reducing the need for additional finishing processes.
Additionally, die casting is a relatively fast and efficient process, allowing for high production rates and low labor costs. The process also generates very little waste material, making it an environmentally friendly option. Finally, die casting can be used to produce parts with a wide range of sizes and shapes, making it a versatile choice for many applications.
What are the limitations of die casting?
While die casting offers many advantages, there are also some limitations to the process. One limitation is that it can be expensive to set up the equipment needed for die casting, making it less suitable for small-scale production runs.
Another limitation is that die casting is best suited for parts that are relatively small in size and have a simple shape. More complex parts may require additional finishing or machining processes, adding to the cost and time required for production. Finally, die casting is not suitable for all materials, as some metals may not be able to withstand the high temperatures and pressures involved in the process.
What industries use die casting?
Die casting is used in a wide range of industries, including automotive, aerospace, electronics, and consumer products. In the automotive industry, die casting is used to produce parts such as engine blocks, transmission cases, and steering components.
In the aerospace industry, die casting is used to produce parts for aircraft engines, landing gear, and other components. In the electronics industry, die casting is used to produce parts for computers, televisions, and other devices. Finally, in the consumer products industry, die casting is used to produce parts for items such as toys, sporting equipment, and kitchen appliances.
What is the difference between hot and cold chamber die casting?
Hot chamber die casting and cold chamber die casting are two variations of the die casting process. In hot chamber die casting, the molten metal is kept in a furnace and injected into the mold cavity using a piston. This process is best suited for materials such as zinc and magnesium, which have a low melting point.
In cold chamber die casting, the molten metal is kept in a separate holding furnace and then injected into the mold cavity using a shot sleeve. This process is best suited for materials such as aluminum and copper, which have a higher melting point. While hot chamber die casting allows for faster production rates and is easier to automate, cold chamber die casting is better suited for larger parts and materials that require higher melting temperatures.
In conclusion, Die Casting is a manufacturing process that involves the use of molten metal. The molten metal is injected into a mold and allowed to cool and solidify. This process is used to create complex shapes and parts that are used in a variety of industries.
Die Casting is a widely used manufacturing process because it is cost-effective, efficient, and produces high-quality parts. It is particularly useful for creating large quantities of parts quickly and accurately.
Overall, Die Casting is an essential part of modern manufacturing. It allows for the creation of complex parts that are used in a wide range of products. Without Die Casting, many of the products we rely on every day would not be possible.
Request a quote today!
[contact-form-7 id="1578" title="Contact form"]
Please compress the file into a ZIP or RAR file before uploading. Alternatively, send through your RFQ by email.
enquires@unitymanufacture.com