Table of Contents
- Understanding Plasticizing in Injection Molding
- Frequently Asked Questions
- What is plasticizing in injection molding?
- What is the purpose of plasticizing in injection molding?
- What are the factors that affect plasticizing in injection molding?
- What are the common problems with plasticizing in injection molding?
- How can plasticizing problems be prevented or solved in injection molding?
Injection molding is a widely used manufacturing process that involves the use of plastic resins to produce a variety of plastic parts and products. However, during this process, the plastic material needs to be melted and then injected into a mold to take a specific shape. This is where plasticizing comes in, as it is the process of converting solid plastic pellets or granules into a molten state, ready for injection molding.
In essence, plasticizing is a critical stage in injection molding, as it ensures that the plastic material is in the right state to be molded into the desired shape. Without proper plasticizing, the plastic parts produced may have inconsistencies or defects, affecting the quality of the final product. Thus, understanding plasticizing in injection molding is vital for anyone involved in the manufacturing process.
Understanding Plasticizing in Injection Molding
Plasticizing is a critical process in injection molding, which involves the melting and blending of plastic materials to form the desired mold shape. It involves the use of high temperatures and pressure to melt and inject the plastic into the mold cavity, where it cools and solidifies to form the finished part. In this article, we will delve deeper into the plasticizing process in injection molding, its benefits, and how it compares to other molding techniques.
What is Plasticizing in Injection Molding?
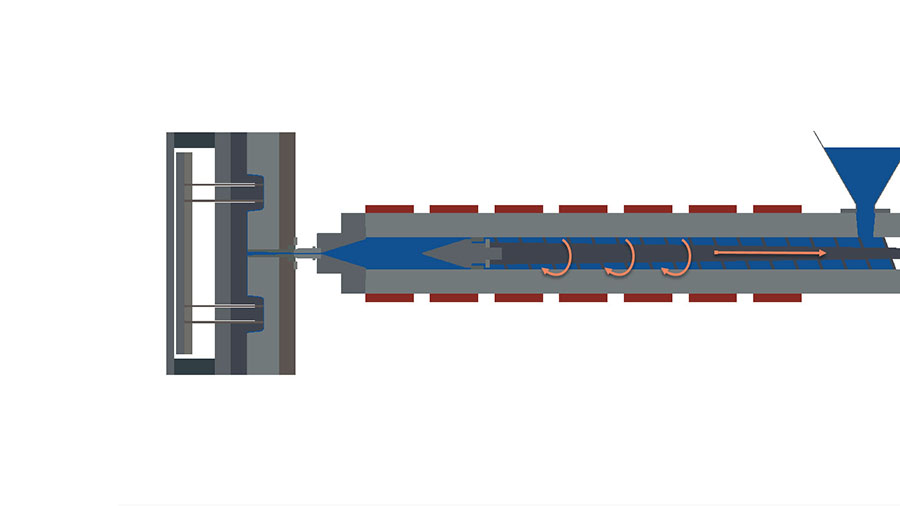
Plasticizing is the process of converting solid plastic pellets or granules into a fluid state by applying heat and pressure. The aim is to create a homogenous plastic melt with a consistent viscosity and temperature suitable for injection molding. The plasticizing process involves three main stages: melting, compressing, and injecting.
During the melting stage, the plastic granules are fed into the injection molding machine’s hopper, where they are heated by the barrel’s heating elements. The heat melts the plastic, which is then compressed by the screw and barrel’s mechanical action. The compression ensures that the melt is free of air pockets and has a consistent viscosity and temperature.
After compression, the plastic melt is then injected into the mold cavity through the nozzle. The injection process involves high pressure and speed, ensuring that the plastic fills the cavity completely and uniformly. Once the mold cavity is filled, the plastic cools and solidifies, forming the finished part.
The Benefits of Plasticizing in Injection Molding
Plasticizing is a critical process in injection molding and offers several benefits, including:
Improved Quality: Plasticizing ensures that the plastic melt is homogenous and free of air pockets, resulting in high-quality finished parts with a consistent surface finish.
Reduced Waste: Plasticizing allows for better control of the plastic melt, resulting in less waste and scrap materials.
Increased Efficiency: The plasticizing process is automated and can be controlled precisely, resulting in faster cycle times and increased production efficiency.
Cost-Effective: Plasticizing allows for the use of a wide range of plastic materials, including recycled plastics, making it a cost-effective molding technique.
Plasticizing vs. Other Molding Techniques
Plasticizing is just one of many molding techniques available in the industry. Other molding techniques include extrusion molding, compression molding, and blow molding. Here is how plasticizing compares to these techniques:
Extrusion Molding: Extrusion molding involves melting plastic pellets and forcing them through a die to form a continuous profile. While plasticizing and extrusion molding both involve melting plastic, extrusion molding is suited for continuous profile shapes, not discrete parts like injection molding.
Compression Molding: Compression molding involves placing preheated plastic material into a heated mold cavity and then compressing it to form the desired shape. While similar to plasticizing, compression molding is better suited for low-volume production runs and simple part shapes.
Blow Molding: Blow molding involves melting a plastic tube, then inflating it within a mold cavity to form the desired shape. Blow molding is better suited for hollow parts like bottles and containers and is not suitable for solid parts like those produced by injection molding.
Conclusion
Plasticizing is a critical process in injection molding, allowing for the efficient and cost-effective production of high-quality plastic parts. Understanding the plasticizing process and its benefits can help manufacturers choose the best molding technique for their specific needs. Whether you opt for plasticizing or another molding technique, it is crucial to work with a reputable injection molding service provider to ensure high-quality parts and reliable production.
Frequently Asked Questions
Injection molding is a complex process that involves several steps to produce high-quality plastic parts. One of the critical steps in the process is plasticizing. Here are some frequently asked questions about plasticizing in injection molding:
What is plasticizing in injection molding?
Plasticizing is the process of melting and mixing the plastic resin pellets or powder with a specific amount of plasticizer to create a homogeneous molten mass. In the injection molding process, the plasticizing unit takes the raw plastic material and transforms it into a molten state, which is then injected into a mold to produce the final plastic part.
The plasticizing unit usually consists of a hopper, a heating element, a screw, and a barrel. The hopper stores the raw plastic material, the heating element melts the plastic, the screw mixes and compresses the molten plastic, and the barrel maintains the temperature and pressure of the molten plastic.
What is the purpose of plasticizing in injection molding?
The purpose of plasticizing in injection molding is to create a homogeneous and molten mass of plastic that can be easily injected into the mold to produce high-quality plastic parts. The plasticizer added during the plasticizing process helps to improve the flowability and processability of the molten plastic, making it easier to inject into the mold and fill all the cavities.
Plasticizing also helps to ensure that the plastic material is free from any air bubbles or voids, which can cause defects in the final part. Additionally, plasticizing helps to control the temperature and pressure of the molten plastic, which is critical for achieving the desired properties and characteristics of the final plastic part.
What are the factors that affect plasticizing in injection molding?
Several factors can affect the plasticizing process in injection molding, including the type of plastic resin, the size and shape of the plastic pellets or powder, the amount and type of plasticizer, the temperature and pressure of the plasticizing unit, and the speed and rate of the screw rotation.
The plasticizing process needs to be carefully controlled and optimized to ensure that the molten plastic has the right viscosity, flowability, and homogeneity, which are essential for producing high-quality plastic parts. Any deviation or variation in these factors can result in defects, such as warping, sink marks, or flash, in the final part.
What are the common problems with plasticizing in injection molding?
Some common problems with plasticizing in injection molding include inadequate mixing or plasticizing, poor homogeneity, degradation of the plastic material, and excessive air entrapment or voids in the molten plastic.
Inadequate mixing or plasticizing can result in unmelted plastic pellets or powder, which can cause flow restrictions and uneven filling of the mold cavities. Poor homogeneity can lead to inconsistent material properties and characteristics, such as color, density, or strength, in the final part. Degradation of the plastic material can occur due to overheating or excessive shear forces, which can cause the plastic to break down and lose its physical properties. Excessive air entrapment or voids can cause defects in the final part, such as bubbles, warpage, or sink marks.
How can plasticizing problems be prevented or solved in injection molding?
To prevent or solve plasticizing problems in injection molding, several measures can be taken, such as selecting the right plastic resin and plasticizer, optimizing the plasticizing temperature and pressure, adjusting the screw speed and rate, and using venting or degassing techniques to remove air or moisture from the plastic material.
In conclusion, plasticizing is a crucial process in injection molding. It involves heating and melting the plastic resin pellets to a molten state, which can be easily injected into the mold cavity. The molten plastic is then cooled and solidified to form the finished product.
With proper plasticizing, the injection molding process can produce high-quality products with excellent surface finishes and dimensional accuracy. However, improper plasticizing can result in defects such as warping, sink marks, and voids.
Therefore, it is essential to have a thorough understanding of plasticizing and its impact on the injection molding process. By optimizing plasticizing parameters such as temperature, pressure, and speed, manufacturers can ensure consistent product quality and reduce production costs.
Request a quote today!
[contact-form-7 id="1578" title="Contact form"]
Please compress the file into a ZIP or RAR file before uploading. Alternatively, send through your RFQ by email.
enquires@unitymanufacture.com